Extrusion and spheronization: How spherical pellets are created
How are pellets created by extrusion and spheronization?
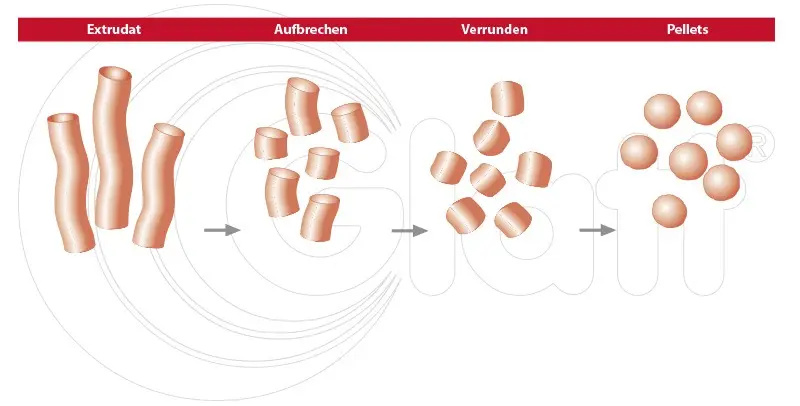
Powdery active ingredients are kneaded with liquid, pressed through an extrusion opening, and turned into pellets by spheronization.
We knead the dry-mixed powdered active ingredients with a liquid to form a moist, homogeneous mass. This is then pressed through an extruder – creating elongated extrusion strands. Their thickness depends on the diameter of the openings in the extrusion plate or basket. For technical reasons, these pellets are larger than 600 micrometers.
What is decisive for the quality of the extrudates? The ratio of liquid to solid as well as the hole size of the extruder. The subsequent drying process ensures the solidification of the pellets.
Even if the spherical shape of the extrudates is not perfect, the uniform surface still creates good conditions for subsequent filming. Incidentally, for many pharmaceutical applications, extruded pellets achieve suitable quality if sufficient microcrystalline cellulose is added.
Extrusion and spheronization – in four process steps:
- moistening of the powder mixture
- formation of cylindrical agglomerates by extrusion
- breaking and rounding of the formed mass (extrudate) into spherical pellets by spheronization
- drying of the finished product
What pellet sizes are possible with extrusion and spheronization?
In principle, we produce any desired pellet size, starting at 600 micrometers. Our pelleting lines can produce particle sizes up to several centimeters with extrusion and spheronization.
Good to know: In the pharmaceutical industry, most applications use pellets of medium particle sizes from 600 to 2000 micrometers. In other industries, pellets can be up to several centimeters in size. We set up pelletizing exactly according to your needs.